CBSE Sample Paper - 02
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT – I
Class – IX Social Science
Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 90
General Instructions:
a) The question paper has 30 questions. All Questions are compulsory.
b) Question numbers 1-8 are one mark questions.
c) Question numbers 9-20 are three marks questions. Answers of these questions should not
exceed 80 words.
d) Question numbers 21-28 are five marks questions. Answers of these questions should not
exceed 100 words.
e) Question number 27 and 28 are based on map questions of three marks each.
f) Question numbers 29 and 30 are Map Based Questions carrying three marks each.
1. What is Livre?
2. Which type of investment is known as human capital investment?
3. How does Population become human capital?
4. How would you agree that Himalayas are the most recent landforms?
5. The workers led by Lech Walesa signed an agreement with the Polish Government which
ended their strike. How many points did the agreement have?
6. How Myanmar is a non-democratic country?
7. Did the ideals of the Quit India Movement contribute to the making of the Indian
Constitution?
8. What is meant by seasonal unemployment?
9. What do you understand by ‘Hyperinflation’?
Or
Who were Soviets? What was their role in the revolution?
10. Highlight three main features of the political system setup after the defeat of Imperial
Germany in the First World War.
Or
Why Socialists were against private property? Explain.
11. Which is most important Longitude of the country? Give reason.
12. In Lakshadweep, there is a bird sanctuary on Pitti island. This island is uninhabited. Should
some people be allowed to live on Pitti island? If they are allowed, what can be the harmful
effects?
13. Explain any three reasons for the significance of rivers for the economy of a country.
14. Which requirement for production is considered the best? Give reason.
15. Describe any three main features of democracy.
16. ‘The South African Constitution inspires democrats all over the world'. Justify the statement.
17. How do democracy provide platform to deal with differences and conflict?
18. From where do the small farmers get capital for farming? How does it affect the farmers?
19. 'Walesa soon emerged as a leader of the striking workers in Poland'. Identify three values
that helped him to lead the strike.
20. What was a ‘Directory’? Why was it removed from France?
21. Explain the main objectives of the Russian Revolutionaries.
Or
What kind of education was given in Nazi schools?
22. India is said to enjoy a strategic position with reference to international trade routes. In your
view, which features provide India a strategic advantage?
23. What is lake? Explain the importance of lakes.
24. Why has democracy spread?
25. Explain five major factors which contributed to the making of our Constitution.
26. What is meant by Green Revolution? Mention some of its features.
27. Give examples to prove that population is an asset for the economy, rather than a liability.
28. What was the contribution of the French philosophers in the outbreak of the Revolution of
1789 in France?
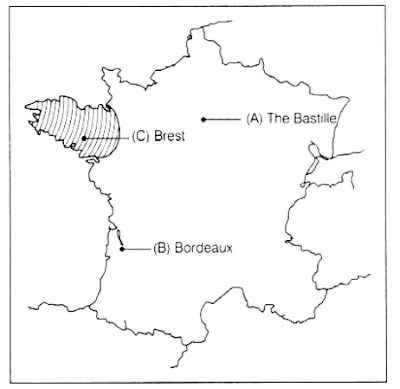
29. Three items A, B and C are shown in the given outline map of France. Identify these items
with the help of the following information and write their correct names on the lines marked
on the map.
(i) A fortress prison stormed by the people of France in 1789.
(ii) Port of France related to the slave trade.
(iii) A region not affected by the Great Fear.

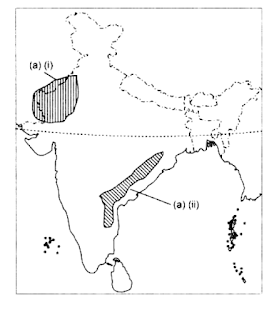
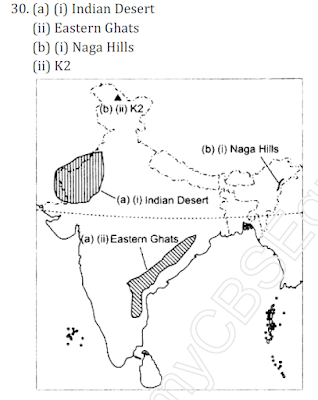
30. (a) Two features are shown on the outline map of India. Identify these features and write
their names on the lines marked on the map.
(i) A physiographic region where Barchans are found
(ii) This region is part of the Deccan plateau
(b) On the map, locate and label the following with appropriate symbols.
(i) A range of hills in Nagaland bordering Myanmar
(ii) The highest mountain peak in the Karakoram Range
Solutions of the Sample paperSUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT – I
Class – IX Social Science
Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 90
General Instructions:
a) The question paper has 30 questions. All Questions are compulsory.
b) Question numbers 1-8 are one mark questions.
c) Question numbers 9-20 are three marks questions. Answers of these questions should not
exceed 80 words.
d) Question numbers 21-28 are five marks questions. Answers of these questions should not
exceed 100 words.
e) Question number 27 and 28 are based on map questions of three marks each.
f) Question numbers 29 and 30 are Map Based Questions carrying three marks each.
1. What is Livre?
2. Which type of investment is known as human capital investment?
3. How does Population become human capital?
4. How would you agree that Himalayas are the most recent landforms?
5. The workers led by Lech Walesa signed an agreement with the Polish Government which
ended their strike. How many points did the agreement have?
6. How Myanmar is a non-democratic country?
7. Did the ideals of the Quit India Movement contribute to the making of the Indian
Constitution?
8. What is meant by seasonal unemployment?
9. What do you understand by ‘Hyperinflation’?
Or
Who were Soviets? What was their role in the revolution?
10. Highlight three main features of the political system setup after the defeat of Imperial
Germany in the First World War.
Or
Why Socialists were against private property? Explain.
11. Which is most important Longitude of the country? Give reason.
12. In Lakshadweep, there is a bird sanctuary on Pitti island. This island is uninhabited. Should
some people be allowed to live on Pitti island? If they are allowed, what can be the harmful
effects?
13. Explain any three reasons for the significance of rivers for the economy of a country.
14. Which requirement for production is considered the best? Give reason.
15. Describe any three main features of democracy.
16. ‘The South African Constitution inspires democrats all over the world'. Justify the statement.
17. How do democracy provide platform to deal with differences and conflict?
18. From where do the small farmers get capital for farming? How does it affect the farmers?
19. 'Walesa soon emerged as a leader of the striking workers in Poland'. Identify three values
that helped him to lead the strike.
20. What was a ‘Directory’? Why was it removed from France?
21. Explain the main objectives of the Russian Revolutionaries.
Or
What kind of education was given in Nazi schools?
22. India is said to enjoy a strategic position with reference to international trade routes. In your
view, which features provide India a strategic advantage?
23. What is lake? Explain the importance of lakes.
24. Why has democracy spread?
25. Explain five major factors which contributed to the making of our Constitution.
26. What is meant by Green Revolution? Mention some of its features.
27. Give examples to prove that population is an asset for the economy, rather than a liability.
28. What was the contribution of the French philosophers in the outbreak of the Revolution of
1789 in France?
29. Three items A, B and C are shown in the given outline map of France. Identify these items
with the help of the following information and write their correct names on the lines marked
on the map.
(i) A fortress prison stormed by the people of France in 1789.
(ii) Port of France related to the slave trade.
(iii) A region not affected by the Great Fear.

30. (a) Two features are shown on the outline map of India. Identify these features and write
their names on the lines marked on the map.
(i) A physiographic region where Barchans are found
(ii) This region is part of the Deccan plateau
(b) On the map, locate and label the following with appropriate symbols.
(i) A range of hills in Nagaland bordering Myanmar
(ii) The highest mountain peak in the Karakoram Range
1. It was a unit of currency in France discontinued in 1794.
2. The investment made in the form of education, training and medical care is known as human
capital formation.
3. Population becomes human capital when there is investment made in the form of education,
training and medical care.
4. The whole mountain system of Himalayas represents a very youthful topography with high
peaks, deep valleys and fast flowing rivers.
5. The agreement which ended their strike was a 21-point agreement.
6. The army rulers of Myanmar are not elected by the people. Those who happen to be in control
of the army become the rulers of the country people have no say in this decision.
7. No, they did not. However, the Socialist Revolution in Russia, the Bill of the Rights of the US
and the ideals of the French Revolution were the contributing factors.
8. Seasonal unemployment occurs when people who are willing to work are not able to find jobs
during some months of the year.
9. With too much of printed money in circulation, the value of German mark fell. As the value of
German mark collapsed, prices of goods soared. The image of Germans carrying cartloads of
currency notes to buy a loaf of bread was widely publicised evoking worldwide sympathy. This
crisis came to be known as ‘hyperinflation’- a situation when prices rise phenomenally high.
Or
Soviet was a council of striking workers and soldiers formed in the February Revolution.
The Petrograd Soviet led the revolution.
It helped the Bolsheviks to seize he power.
They gained victory in the civil war.
10. The defeat of Imperial Germany and the abdication of the emperor gave an opportunity to
parliamentary parties to recast Germany polity.
A National Assembly met at Weimer and established a democratic constitution with a federal
structure.
Deputies were now elected to the German Parliament or Reichstag, on the basis of equal and
universal votes cast by all adults including women.
Or
Socialists were against private property and thought that it was the mail cause of all social ills
of the time.
Individuals owned the property that gave employment but the propertied were concerned
only with personal gain and not with the welfare of those who made the property productive.
So id society as a whole rather than single individual controlled property, more attention
would be paid to collective social interests. Socialists wanted this change and campaigned for
it.
11. 82°30'E, longitude is the most important longitude of our country.
To avoid confusion and chaos in all activities to be caused by having a different local time for
different places.
The central Meridian 82°30'E is taken as the Indian Standard Time.
It is accepted all over the country for uniformity of time.
12. Humans should not be allowed to inhabit Pitti island, as this will affect the breeding of the
birds on it; the presence of humans along with their activities will disturb them, resulting in
the birds moving elsewhere.
The harmful effects of human activity are:
(i) Pollution of freshwater sources on the island due to human activity. The birds will not get
clean water to drink.
(ii) Hunting of birds for food by the humans will reduce the birds’ population on the island.
13. The role and significance of rivers for the economy of a country are as follows:
(i) Water from the rivers is a basic natural resource, essential for various human activities like
agriculture, domestic use, industrial consumption etc.
(ii) Rivers are used for hydro-power generation and irrigation. This is of special significance
particularly to a country like India, where agriculture is the major source of livelihood of
the majority of its population.
(iii) Rivers are used for cheap transportation of people andgoods. This also develops the trade
capability of the country.
14. Human capital is considered to be the best.
This is because man has knowledge and ability to put together land, labour and physical
capital.
And produce an output either to use self or to sell in the market.
Human capital is the stock of skill and productive knowledge embodied in them.
15. Democracy is a form of government in which the rulers are elected by the people.
The features of democracy are:
(i) Democracy is a form of government in which the rulers are elected by the people.
(ii) A democracy must be based on a free and fair election, where those currently in power
have a fair chance of losing.
(iii) In a democracy, each adult citizen must have one vote and each vote must have one value.
16. After two years of discussion and debate, the Constitution of South Africa was finalised. It gave
its citizens the most extensive rights available in any country.
The Constitution writers included everybody; no one has been treated differently, irrespective
of whatever they have done in the past.
The Constitution was based on social equality and justice. Thus, the Constitution inspires
democrats all over the world.
17. Democracy provides the method to deal with differences and conflict.
In any society people are bound to have differences of opinion and interests. These differences
are particularly sharp in country like ours which has an amazing social diversity.
Democracy provides the only peaceful solution to this problem. In democracy no one is the
permanent winner. No one is the permanent looser. Different groups can live with one another
peacefully.
18. The small farmers have to borrow money to get capital for farming, either from large farmers,
the village moneylenders, or the traders who supply various inputs for cultivation. However, it
affects these farmers adversely, because the rate of interest on such loans is very high. The
small farmers repay these loans and the interest with great difficulty, or in case of a bad
harvest, fall into a debt trap.
19. The values that helped Walesa to lead the strike were:
(i) His ability to win the trust and confidence of the shipyard workers. This was possible
because he had himself been a shipyard worker before he was dismissed from service for
demanding higher pay.
(ii) His love for freedom and democracy. He wanted to be free to form a trade union
independent of the Communist party.
(iii) His determination to provide justice to the workers, despite not being a current member
of the shipyard’s workforce.
20. After the fall of Jacobins, a new Constitution was formed which denied the right to vote to nonpropertied
men. It provided two elected legislative Councils, who appointed a Directory, an
executive made up of five members. However, the directors often clashed with the legislative
councils and were finally dismissed. With this, political instability emerged in France which
gave rise to a military dictator, Napoleon Bonaparte.
21. Revolutionaries demanded that Russia should withdraw from the World War.
The demanded that land should go to the tiller.
The want to establish government farms.
The demanded that banks and industries should be nationalized.
The demanded an improvement in the working conditions of workers and wages also.
The demanded that non Russian should be given equal status so that they could work for the
development of Russia.
Or
(i) Jew teachers were dismissed from the schools.
(ii) Children were segregated. Germans and Jews neither could sit together nor play together.
(iii) Subsequently, undesirable children-Jews, the physically handicapped and Gypsies were
thrown out of schools.
(iv) School textbooks were rewritten.
(v) Racial Science was introduced to justify Nazi’s ideas of race.
(vi) Children were taught to be loyal and submissive, to hate the Jews and worship Hitler.
(vii) Boxing was introduced as Hitler believed that it could make children iron hearted, strong
and masculine.
22. India occupies a unique position on the globe. It enjoys a unique proximity with Europe, Africa
and Australia. The Indian landmass has a central location between East and West Asia. India is
the southward extension of Asia; thus, it forms the South-Central Peninsula of the world’s
largest continent. The Deccan Peninsula, India’s southward extension, protrudes into the
Indian Ocean and divides it into two seas, the Arabian Sea on the West and the Bay of Bengal
on its East.
The Deccan Peninsula helps India to establish easy contact with West Asia, East Africa and
Europe from the Western coast and with South-East Asia, East Asia and Australia from the
Eastern coast. India has the longest coastline on the Indian Ocean. These geographical features
provides India a significant edge in international trade.
23. A lake is a large body of water that is entirely surrounded by land. Lake water can be fresh or
sometimes salty or saline.
The importance of lakes is stated in its benefit below:
(i) Lakes help to regulate the flow of rivers.
(ii) During heavy rainfall, lakes prevent flooding and during the dry season, lakes help to
maintain an even flow of water.
(iii) Lakes can also be used for developing hydel power.
(iv) Further they moderate the climate of the surroundings, maintain the aquatic eco-system,
enhance natural beauty, help develop tourism and provide recreation.
24. Democracy has spread and expanded through the 20th century because people consider it the
best form of government. The examples are:
(i) In Chile, a democratic government existed until September 1973, when it was overthrown
in a military coup. After ruling for 17 years, the military was overthrown in a referendum
and democracy was restored.
(ii) In Poland, a similar situation occurred when the Communist government was replaced by
military rule with Martial Law in force. But in 1990, this was replaced by democratic rule.
(iii) At the beginning of the 20th century, only a handful of the governments were democratic.
This increased somewhat by 1950, but by 2005, more than 140 governments were
democratically elected.
All these examples show that democracy has expanded through the 20th century.
25. The making of the Constitution for a huge and diverse country like India was not an easy affair.
The country was born through a partition which was a traumatic experience. The major factors
which contributed to the making of our Constitution were
(i) At that time, people of India were emerging from the status of subjects to that of citizens.
They became conscious of their rights and privileges.
(ii) Our leaders gained confidence to learn from other countries, but on our own terms. Many
of them were inspired by the ideals of the French Revolution.
(iii) They were also influenced by the practices of Parliamentary democracy in Britain and the
Bill of Rights in the US.
(iv) Social Revolution in Russia inspired many Indians to think of shaping a system based an
social and economic equality.
(v) The makers of the Constitution were not simply imitating the Constitution of other
countries.
At each step, they were questioning whether the values and ideals they accepted suited our
country or not.
26. The introduction of High Yielding Varieties (HYV) of seeds and the increased use of chemical
fertilisers and irrigation are collectively known as the Green Revolution.
It provided the increase in production needed to make India self-sufficient in food grains, thus
improving agriculture in India.
High yielding wheat was first introduced to India in 1968 by American agronomist Norman
Borlaug. Borlaug has been called as father of the Green Revolution, but MS Swaminathan is
known as the ‘Father of Green Revolution in India.
Thus, Green Revolution is the term used to describe a new strategy of agricultural
development introduced in the late 1960s in India. It brought about significant increase in food
production in India.
Major features ofGreen Revolution in India were:
(i) Use of High Yielding Varieties (HYV) of seeds. HYV seeds promised to produce much greater
amounts of grain on a single plant.
(ii) Use of advanced technology, chemical fertilisers, pesticides and a well-developed system of
irrigation.
(iii) This revolution solved the food crisis in India and made India self-sufficient in food grains.
(iv) This led to higher income growth and reduced poverty.
27. Population becomes human capital when an investment is made in it through education,
training and medical care. Human capital is a productive asset, rather than a liability, as given
in the examples below:
(i) Doctor A person trained for this profession cures ill people and helps maintain good health
of the people.
(ii) Engineer Persons who are trained as engineers are useful to the nation in various fields
like construction, industry, Information Technology etc.
(iii) Teacher Trained teachers are much in demand in the educational institutions of the
country. They are helping to develop the next generation of productive assets for the
country.
(iv) Tailor A person trained in tailoring produces clothes which people wear, thus becoming a
productive asset.
28. The revolutionary ideas of philosophers encouraged people to fight for their rights.
(i) Voltaire believed that man’s destiny was in his own hands.
(ii) John Locke criticised the divine and absolute rights of the rulers.
(iii) Rousseau put forward the idea of formation of a government based on a social contract
between people and their representatives. Men had the right to change their government if
they were not satisfied with it.
(iv) Montesquieu believed that all powers should not be concentrated in one person’s hand.
They should be divided between the Legislature, the Executive and the Judiciary.
The ideas of these philosophers were discussed by common people in salons and coffee-houses
and inspired them to fight for their rights.
No comments:
Post a Comment